This is the second instalment in the ISO 19011 audit series which looks at activities required to successfully prepare for an integrated management audit. In this post we will look at pre-audit activities and elaborate on the graph below:
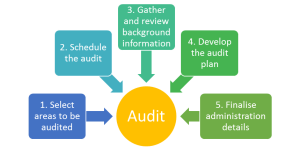
Scheduling an audit
Initial contact is made with the auditee to:
- Confirm the authority to conduct the audit and schedule audit
- Provide information on the audit objectives, scope, methods and composition of audit team
- Request access to relevant documents and records for planning purposes
- Determine applicable legal and contractual requirements and other requirements relevant to the activities and products of the auditee.
Gather and review background information
In order to prepare for an audit, the necessary documentation for the management system needs to be reviewed. The documentation review should include:
- Management system documentation and records
- Checklists
- Audit sampling plans
- Forms for recording information such as records of meetings, audit findings and supporting evidence
- Previous audit reports
It is important to gather this information on processes and functions in order to gain an insight into the extent of the system documentation and to detect possible gaps in the management system as well as to assess the audit objectives and scope.
Audit Plan
An audit plan should be developed by the audit team leader based on the information obtained from the audit programme and from the documentation provided by the auditee. This plan should facilitate the efficient scheduling and coordination of audit activities in order to achieve the objectives effectively.
The audit plan should include but is not limited to the following:
- Objectives
- Scope
- Criteria and any reference documents
- Locations, dates and duration of audit activities
- Roles and responsibilities of the audit team members
- Allocations of appropriate resources to critical areas of the audit
- Audit report topics
- Any follow-up actions from a previous audit
- Any follow-up activities from the planned audit
The audit team leader will assign responsibility for auditing specific processes, activities or functions to each team member.
Audit team members are obliged to collect and review the information relevant to their audit activities and prepare work documents, such as checklists, audit sampling plans and forms for recording information for the purpose of recording audit evidence. The work documents need to be retained for the duration of the audit or for as long as specified in the audit plan.
Once administration details have been finalised, it is then time to look at the activities required to carry out the audit which is the focus of our next blog post in this series.
Link to previous blog available here:
Preparing for an Integrated Management Systems Audit: ISO 19011:2011
Sources:
ISO 19011:2011 Full Standard: http://www.cnis.gov.cn/wzgg/201202/P020120229378899282521.pdf
ISO 19011:2011 Overview: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=50675


