The ISO 19011:2011 standard outlines the process for auditing an integrated management system.
This includes:
- The principles of auditing
- Managing an audit programme
- Advice on conducting an audit on a management system
It also advises on the assessment of individuals involved in the audit process including the lead auditor and audit team.
This standard is applicable to all organisations that need to conduct internal or external audits of management systems.
This aim of ISO 19011 is to save time, effort and money by:
- Securing agreement on the goals for individual audits within an audit programme.
- Reducing duplication when conducting audits
- Ensuring audit reports follow the best format and contain all the relevant information
- Evaluating the competence of the members of the audit team against appropriate criteria
Types of audits:
- First party: Internal – the organisation audits its own systems. This measures the strengths and weaknesses of the management system against the system requirements.
- Second party: Supplier – audits of other facilities. One organisation audits the another with which it has a contract to supply goods and services.
- Third party: Certification – independent of the organisation being audited. This verifies compliance with specific standards.
The Principles of Auditing:
The principles of auditing ensure that an audit is an effective and reliable tool in support of management policies and controls, by providing information on which an organization can act in order to improve its performance.
The principles outlined by ISO 19011:2011 include:
- Integrity
- Fair presentation
- Due professional care
- Confidentiality
- Independence
- Evidence-based approach
Managing an Audit Programme:
An organization which needs to conduct audits should establish an audit programme. This will determine the effectiveness of the management system. The magnitude of the audit programme should be based on the size and nature of the organisation being audited, as well as the functionality, complexity and level of maturity of the management system which is subject to the audit.
Priority should be given to allocating programme resources to auditing the issues of significance within the company such as hazards related to health and safety, key characteristics of product quality or significant environmental aspects.
The audit programme should include information and resources necessary to organise and conduct audits effectively and efficiently within the specified time frame. Typical of the information to be included in the programme is the following:
- Objectives for the programme and individual audits
- Schedule of audits
- Audit procedures or protocols
- Audit criteria
- Audit methods
- Selection of audit teams
- Logistics such as travel and accommodation
- Processes for handling confidentiality, information security etc.
Conducting an Audit:
When an audit is initiated, responsibility for conducting the audit resides with the assigned audit team leader until the audit is completed.
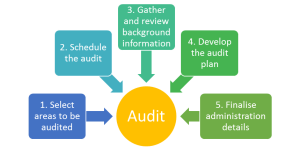
Pre-audit activities may include:
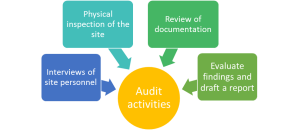
Audit activities will include:
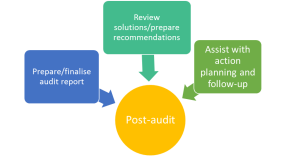
Post-audit activities include:
The next blog in this series will focus on pre-audit activities.
Sources:
ISO 19011:2011 Full Standard: http://www.cnis.gov.cn/wzgg/201202/P020120229378899282521.pdf
ISO 19011:2011 Overview: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=50675
Audit types: http://www.aatb.org/files/Audit%20Types%20presentation%20-%20Sue%20Brewster.pdf